Behind the Block: PoW vs PoS
Part 2 - What is Proof of Stake, how it works, how to choose staking protocols.
Hey, it’s so great to have you back. Did my last post make you feel that maybe mining has a high barrier to entry, it needs expensive equipment and it takes too much electricity? That’s exactly what some miners felt back in the day and some of them transitioned to a more energy efficient solution: PROOF OF STAKE (PoS).
A landmark event in the blockchain world was Ethereum's switch to PoS on September 15, 2022. This move, aimed at reducing energy consumption and improving scalability, has introduced over 200,000 validators into the Ethereum network initially. Since this is the most well-known PoS protocol, it makes sense to explain it.
What’s Changed from Mining to Staking?
In the old system (PoW), members (miners) competed to solve complex puzzles to earn the right to update the ledger (blockchain). It required a lot of computer power and energy. Ethereum's new system doesn't need these energy-draining puzzles. Instead, members (now called validators) who want to help maintain the ledger must "stake" some of their Ethereum (ETH) as a sort of promise that they'll do their job well.
How Does Staking Work?
To become a validator, you need to lock up 32 ETH, to be precise. Think of this as your pledge that you’re serious and not just messing about. This pledge acts like a security deposit. When the network needs someone to update the ledger with new transactions, it doesn’t just pick anyone. It randomly chooses from the pool of members who’ve made a pledge (stake), favouring those who've staked more money. The idea is, the more you stake, the more likely you are to be picked.
If chosen, your role as a validator is to propose a new page of the ledger (a block of transactions). Then, other validators check your work (this is called attesting). If they agree you’ve done it right, your update gets added to the ledger. As a reward, you earn some transaction fees and possibly some extra Ether.
But what if someone tries to cheat?
Breaking the rules comes with consequences. If a validator tries to cheat or does a sloppy job, they can lose some or all of their pledged Ether. This penalty helps keep everyone honest. Think of it as a lottery where your chances of winning are not just random but also based on how much you're willing to invest in the lottery’s success. In this setup, instead of buying tickets, you pledge money to ensure the game is fair. The more money you pledge, the higher your chances of being selected to distribute the prizes—and earn a bit yourself. But, if you try to mess with the lottery or fail to do your job, you'll lose your investment.
Why this new method?
This change aims to make the whole process more democratic, secure, and environmentally friendly. Validators are super important in making sure that the Ethereum network runs smoothly, accurately, and fairly. This shift from PoW to PoS is not just a technical update but a significant improvement in how Ethereum functions.
As of March 2024, the Ethereum network has reached a significant milestone with over one million validators actively participating in its proof-of-stake system. This large number of validators reflects strong community support and confidence in Ethereum's security and decentralisation under the PoS consensus mechanism.
DID YOU KNOW?
Ethereum is not the first Proof of Stake protocol!
In 2012, a new protocol emerged, PeerCoin, that pioneered a hybrid approach to blockchain security by combining Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS). Initially, PoW was used for distributing coins fairly among users, much like earning wages for work done. Later, the system shifts to PoS, where the creation of new blocks and network security depend on the quantity of coins users hold and the duration they hold them, encouraging saving over spending.
By combining PoW and PoS, Peercoin aimed to create a more sustainable and inclusive way to manage its currency, setting a precedent for future cryptocurrencies to think beyond traditional mining methods.
To date, PeerCoin maintains a low-profile yet stable presence in the cryptocurrency landscape. While it's not in the spotlight like larger cryptocurrencies, it continues to be active.

Thinking about staking your crypto?
It's a great way to earn rewards, but it's not as straightforward as just locking up your coins and forgetting about them. Let's chat about what you should consider to see if it's right for you:
What You'll Earn (APY/Return on Stake): imagine this as the interest rate on a savings account. The higher it is, the more you'll earn from staking your crypto. But, high rewards can also mean higher risks, so think about how stable the project is before jumping in.
Minimum Investment: some crypto projects ask you to stake a hefty amount to start. Make sure this fits your budget.
Lock-up period: this is how long your crypto will be tied up. Shorter lock-up periods mean you can get your crypto back quicker, but often the rewards are less. Other protocols have longer withdrawal times and this can impact your profitability if the prices go down by the time your cryptocurrency is returned to you.
Price volatility: the value of your staked coins can fluctuate, affecting your returns, so keep this in mind.
Inflation's impact: just like money loses value over time with inflation, the same can happen with crypto. If the crypto's inflation is high, your staking rewards might not be as valuable as you think.
Slashing risks: in some networks, if something goes wrong (like your staking computer/server goes offline), you could lose some or all of your staked crypto. It's a bit like a performance bond – you need to keep things running smoothly, or it'll cost you. As a solo validator you need to have good internet connection with 100% uptime to avoid penalties. Or else buy a server rack space in a data centre.
Network security and number of validators: more validators usually mean a healthier, more secure network. It's similar to having more security guards at a concert – it generally makes things safer.
Validator's track record: if you're using a staking service, pick someone reliable. Think of it like choosing a babysitter; you'd want someone trustworthy.
Your say in the project: some staking rewards come with voting rights in the project. If having a say in the project's future matters to you, this could be a big plus.
How easy is it to stake?: consider how much tech know-how you need to stake. Direct staking might be more profitable but can be more complex compared to using a staking service.
The project's health and vision: look beyond immediate returns. What's the project's mission? Is the team behind it solid? Think of it as investing in a business – the fundamentals matter for long-term success. Educate yourself on basic financial terms, it will help.
In a nutshell, staking is a balancing act between potential earnings and the risks and efforts involved. Like any investment, it's crucial to do your homework before you commit. Check out the project thoroughly and make sure it matches your investment style and goals.
Interested in learning how to research and strategise your cryptocurrency investments?
Send me a message or click the link below to get started!
What other staking protocols are there?
Let’s take a fun and straightforward look at some major cryptocurrency projects that use a system called Proof of Stake (PoS) to keep things running smoothly. Each project has its unique twist on this technology, which helps them secure their networks and manage who gets to record new transactions.
Tezos (XTZ): Tezos uses a special version of PoS called Liquid Proof of Stake (LPoS). In Tezos, if you own tokens, you can participate in the network by either becoming a validator (fondly called a "baker") or by lending your tokens to a baker without giving them away. This setup makes participating in Tezos both inclusive and flexible, and it’s designed to constantly improve itself through community-driven upgrades.
Solana (SOL): Solana brings something really cool to the table with Proof of History (PoH), combined with PoS. PoH helps confirm the order and time of transactions, acting like a digital timestamp. This, along with PoS, makes Solana super fast and efficient, capable of handling thousands of transactions in a blink!
Cardano (ADA): Cardano’s take on PoS is called Ouroboros and is built to be both secure and scalable, making it a solid foundation for running applications that decentralize power from central authorities. Time in Ouroboros is divided into epochs and slots, which are specific periods when new transaction blocks can be added. This is all managed by slot leaders, chosen based on the amount of ADA they hold.
Polkadot (DOT): Polkadot uses a system known as Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS). Here, you have validators and nominators. Validators do the heavy lifting by processing transactions, and nominators back them by staking DOT on them. This encourages a diverse group of validators and adds an extra layer of security to the network.
These are just a handful of projects showing just how versatile and adaptable PoS can be, each tailoring the mechanism to meet their specific needs and goals. They're pushing the boundaries of how blockchains can function more efficiently, securely, and democratically.
My thoughts on PoW and PoS
My word of advice, regardless of where you choose to put your money, would be to be careful, educate yourself, and calculate your risk and investment needed, with a good margin error and to stick to your values.
Thinking of making money quickly by launching yourself into buying expensive mining hardware, for a coin that just released without knowing if it will ever be on the market, is highly risky and I wouldn't advise a novice doing it, unless you have the money and you don’t mind the risk of losing it.
The same goes for staking: although proof of stake is more energy efficient it doesn't mean all protocols are created equally secure or decentralised, especially when the protocol is just starting or if the number of validators is small.
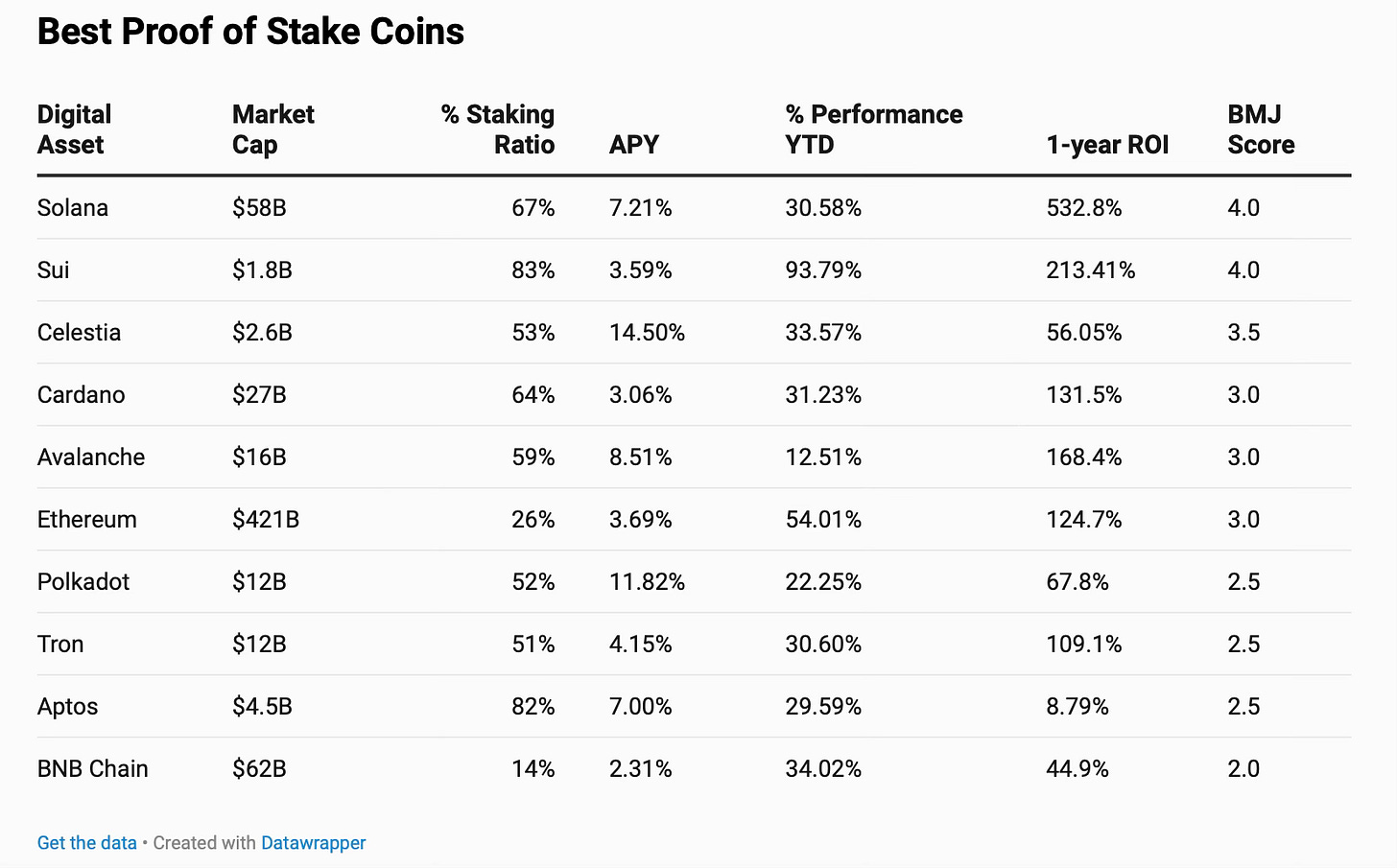
One important thing to consider is the ratio between the market capitalisation (overall value of that cryptocurrency in the market) and the percentage of coins staked (staking ratio). If the market cap is low, the staking ratio should be high. For a cryptocurrency with a large market cap, having a medium to high staking ratio is the safest for you as investor. Image above is an illustration of how ETH is considered extremely secure, with a large market cap and a medium staking ratio.
Still confused? I can help you with my 1-2-1 sessions. Don’t waste time, message me.
Solo staking can be challenging, especially if you’re starting with a small amount of capital. This is why many people favour using staking service providers like Lido, Kraken, Coinbase, RocketPool and others, as you can invest (stake) any amount. Of course, your rewards (APY/interest earned) will be proportional to your staked amount.
In this case, you have to consider that these are third-party businesses that don’t run on blockchain and you will have to rely on the security of their platforms. However, this can be a starting point, an alternative available for investors starting small or who are afraid or intimidated to start directly on blockchain protocols.
I hope this post empowers you to make informed decisions and actively shape the future of cryptocurrency. 🙏❤️





